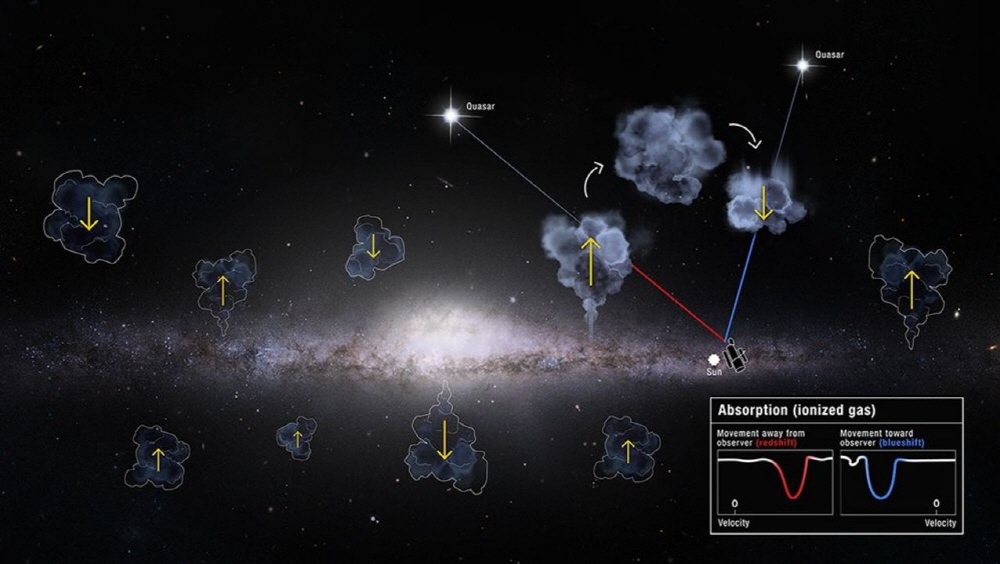
Recent research shows that the galaxy is inhaling more gas than it exhales. The Milky Way inhales and pours out large amounts of ionizing gas, plasma. It has been thought that the amount of gas inhaled and the amount of gas discharged have remained similar so far.
The space between galaxies and galaxies is surrounded by ionizing and neutral gases. Gas can be said to be a kind of natural resource that makes the galaxy a star material. The gas absorbed by the galaxy forms stars, and it can be said that there is a large circulation that is eventually discharged by a supernova explosion or solar wind.
Should the absorbed gas and the discharged gas amount match for this circulation to continue? However, as a result of calculating the amount of gas based on observations with the Hubble Space Telescope, the unexpected result was that the galaxy is sucking in more gas than it exhales.
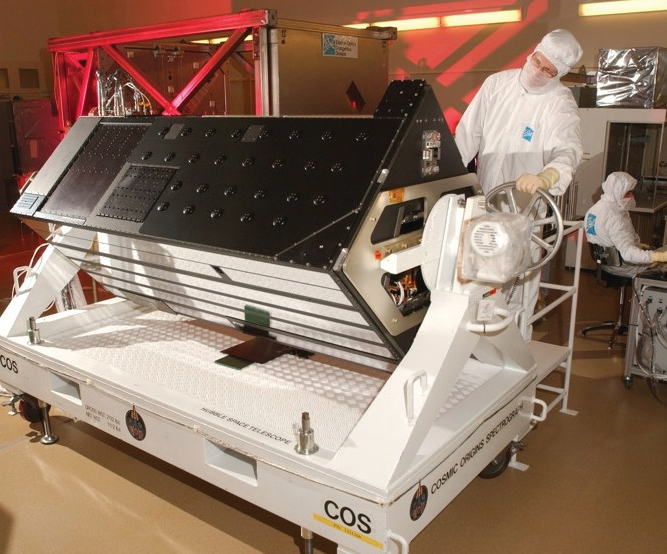
The Hubble Space Telescope is equipped with an equipment called the Space Origin Spectroscope. It is mainly used to observe the distant universe far from the galaxy. The study focused on a galaxy in front of a distant universe. Space Origin Spectroscopy selected 270 images of the galaxy based on 10-year data collected from 2009. 178 of these images show clouds of gas moving at a rate faster than the rotational speed of our galaxy.
It is impossible to identify the gas cloud directly, but it is possible to spot and visualize it with shadows by performing spectroscopic observations of the bright galaxy in the distance. As light hits and absorbs the gas cloud while it reaches Earth, the absorbed light waves are reflected in a shadow, allowing the gas to be seen. In addition, the Doppler shift of the gas cloud was checked to determine whether the gas was sucked in or discharged. It is said that the wavelength of light is blue when it is gathered nearby, and turns red when it is going far away.

As a result of calculating the speed at which 187 gas clouds were sucked or discharged into our galaxy, it was found that the suction volume was higher. This result can be said to support the fact that the actual gas is being recycled in and out of the galaxy.
However, it is not yet clear why the absorption amount is unbalanced with the emission amount, whether it is the most inhalation in the galaxy’s lifetime. The researchers say they may inhale gas from intergalactic space, or from smaller galaxies near the silver car. However, since this study is a result of cutting and analyzing a moment, it is not known how the rate of gas absorption and the rate of discharge change over time.
The space origin spectrometer is only observing in ultraviolet light, so if the wavelength of light is changed, different results may occur. Originally, only high-speed moving gas clouds were investigated, but if we investigated low-speed gas clouds, the results may have been completely different. Related information can be found here .

















Add comment